With the 149th American Fisheries Society Meeting jointly in full swing with The Wildlife Society in Reno, Nevada this week, we decided a re-run of a previous post about a topic that could impact both fish and wildlife was appropriate. In addition, this post is timely as it puts the potential consequences of the recent and continuing roll back on environmental regulations into perspective.
By: Dana Sackett, PhD
Legacy is defined as something that is inherited by one generation from the previous. While some legacies are better than others, not all are good. Legacy pollutants are one of the bad ones. These pollutants stick around to cause problems well after they are released into the environment. Indeed, they often continue to cause harm even after they are banned by regulation. Legacy pollutants have three common attributes that make them particularly problematic: they are Persistent, Bioaccumulative, and Toxic (called PBTs for short). Infamous legacy pollutants include: polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), dioxins and furans, lead, methylmercury, chromium, and some existing and banned pesticides.

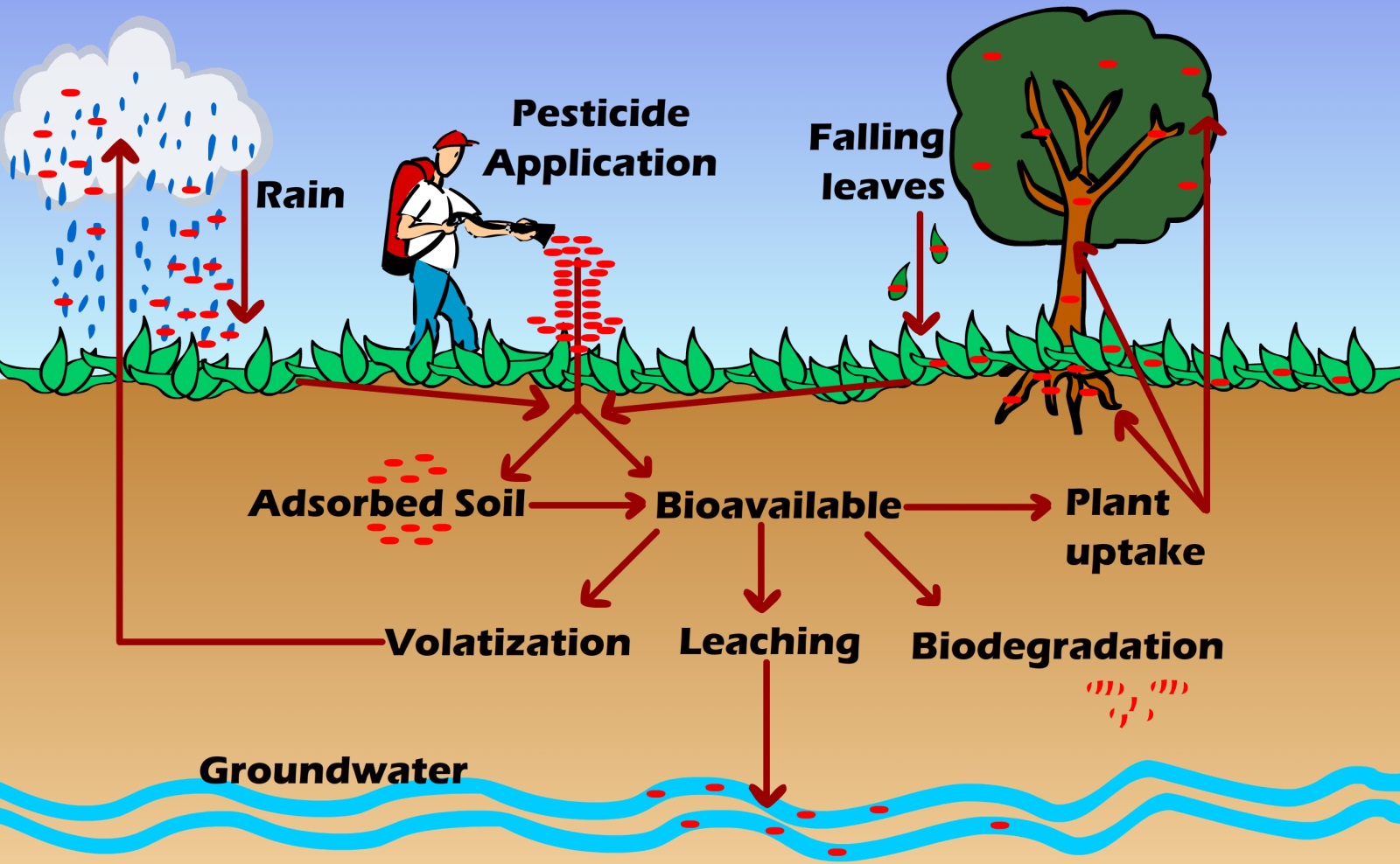
The first characteristic, persistent, is obviously problematic because they do not break down or decompose easily in the environment. Not as obvious, but a natural consequence of being persistent, is that they can travel great distances (even globally via equipment, products, food, or natural forces) as they continue to cycle through the environment. This allows remote ecosystems that are far from the source of a legacy pollutant to be contaminated. Persistence is often measured by determining the half-life of a pollutant, which is the amount of time it takes for half of an amount of the pollutant to degrade.

Bioaccumalative is the second common characteristic of legacy pollutants. This concerning characteristic is because many legacy pollutants do not dissolve in water but instead combine with or dissolve in fats (chemicals that do this are called lipophilic). This makes these pollutants resistant to environmental degradation and also allows them to easily bioaccumulate in food chains.
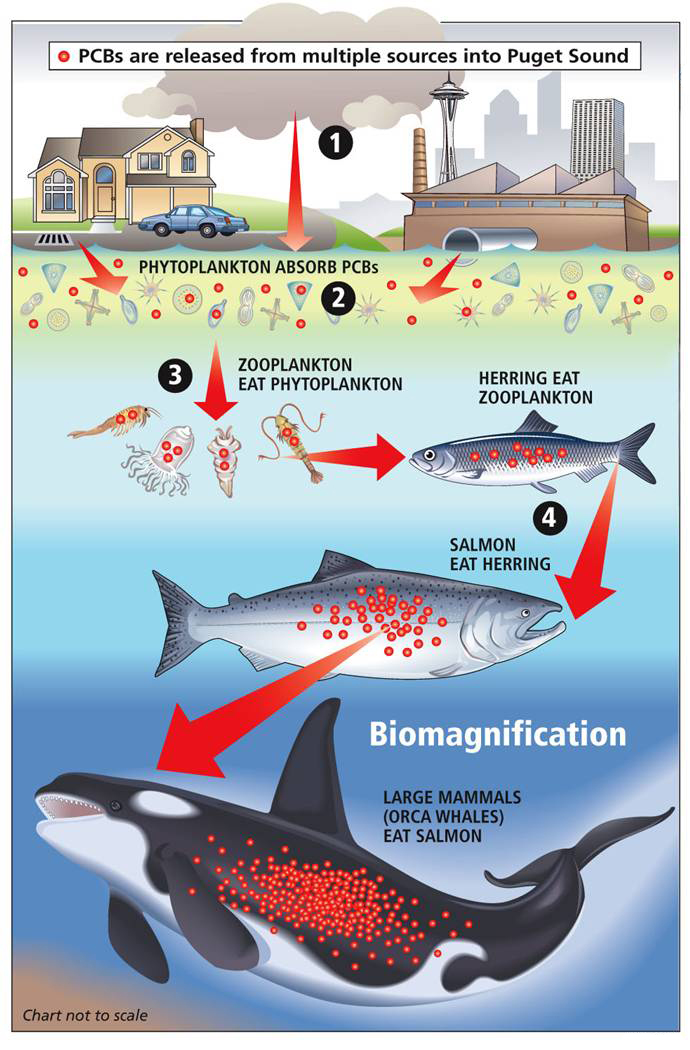
Beyond being persistent and bioaccumalitve, the third defining characteristic of legacy pollutants is the most alarming: they are toxic at very low concentrations. The individual toxic effects of these contaminants are also generally well known and wide ranging for fish, wildlife, and people. Adverse effects have been noted to impact nervous, reproductive, endocrine, and immune systems; with many also being strongly carcinogenic.
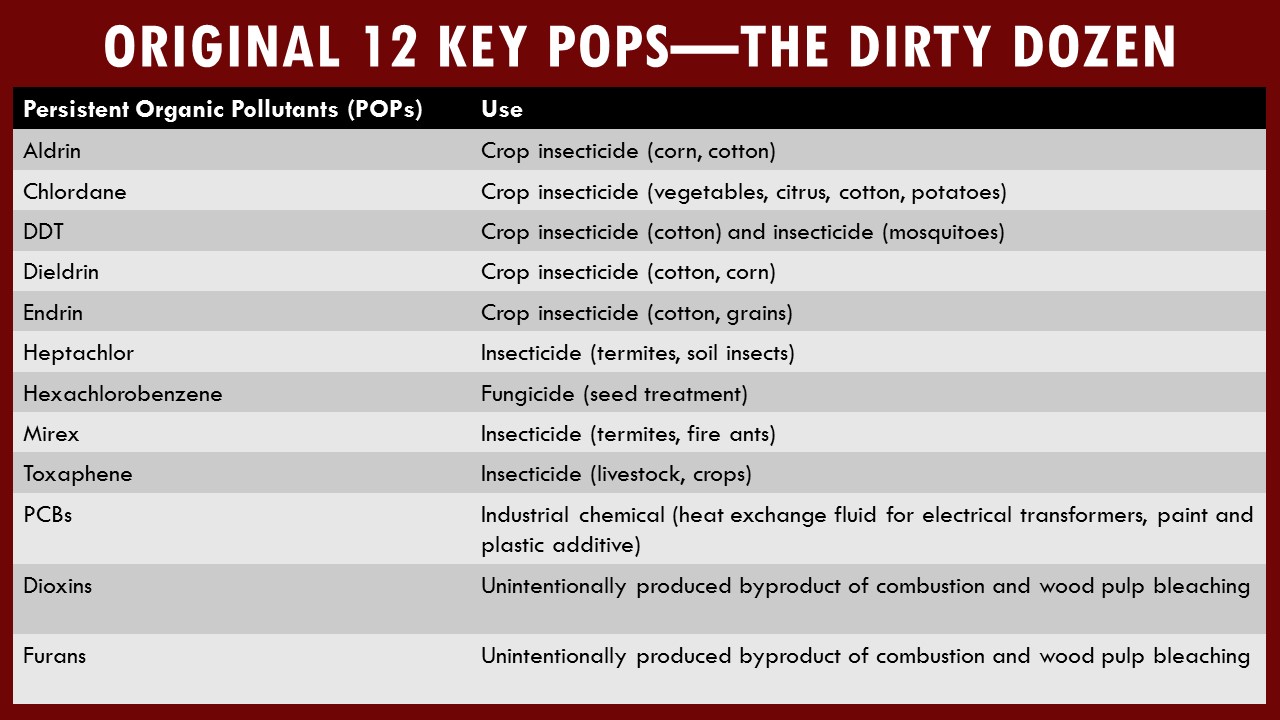
Legacy contaminants are often used and widespread before we identify the full extent of the damage they can do to the health and well-being of our fish, wildlife, and environments as a whole. This is why regulations and programs that prevent the discharge of these legacy pollutants are so important. The US Environmental Protection Agency is responsible for evaluating the associated risks of new and existing chemicals; ensuring they do not have these troubling characteristics. The USEPA is also responsible for finding ways to prevent or reduce pollution from getting into the environment through programs under the Toxic Substances Control Act and the Pollution Prevention Act.
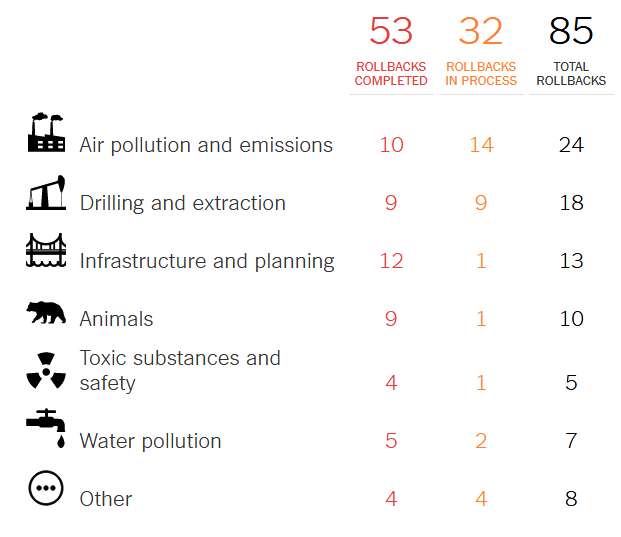
Legacy pollutants are inherently a risk to future generations. This is why the recent loosening of environmental regulations (for example federal cutbacks in environmental protection policies and programs) is a concerning trend. Even a short few years of deregulation could have impacts that affect generations to come.
A full list of the environmental regulations that have been and are being rolled back can be found here.
Resources and References:
Gramatica P, Papa E. 2007. Screening and ranking of POPs for global half-life: QSAR approaches for prioritization based on molecular structure. Environmental Science and Technology 41:2833-2839.
Hutchinson TH, Lyons BP, Thain JE, Law RJ. 2013. Evaluating legacy contaminants and emerging chemicals in marine environments using adverse outcome pathways and biological effects-directed analysis. Marine Pollution Bulletin 74:517-525.
McGoldrick DJ, Murphy EW. 2016. Concentration and distribution of contaminants in lake trout and walleye from the Laurentian Great Lakes (2008-2012). Environmental Pollution 217:85-96.
Click to access iisg0520_glla.pdf
https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/pages/frontline/poisonedwaters/themes/legacy.html
https://www.nap.edu/read/12743/chapter/7
https://news.nationalgeographic.com/2017/03/how-trump-is-changing-science-environment/
https://archive.epa.gov/region09/waste/archive/web/html/pbts.html
Click to access anthropogenic.pdf
https://ecology.wa.gov/Waste-Toxics/Reducing-toxic-chemicals/Addressing-priority-toxic-chemicals
